Choline helps your brain make acetylcholine (for memory and focus) and phospholipids (for healthy cell membranes). Top everyday food sources in U.S. kitchens include eggs (≈147 mg/egg), beef liver (≈356 mg/3 oz), salmon and white fish, chicken breast, shrimp, soy/edamame, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and Brussels sprouts. Aim for roughly 425 mg/day (women) and 550 mg/day (men) from real foods. Office of Dietary Supplements

Table of Contents
- What Is Choline (and Why Your Brain Loves It)
- How Much Choline Do You Need? (U.S. guidelines)
- The 7 Best Choline-Rich Foods
- A Real-World Celebrity Snapshot
- Simple U.S. Meal Ideas (No Supplements Needed)
- 10+ Quick Q&A
- Sources & Further Reading
What Is Choline (and Why Your Brain Loves It)
Choline is an essential nutrient. Your body uses it to make acetylcholine (a neurotransmitter crucial for memory, learning, and muscle control) and phosphatidylcholine/sphingomyelin (key parts of cell membranes, including brain cells). You make a little in your liver, but not enough, so diet matters. Office of Dietary Supplements

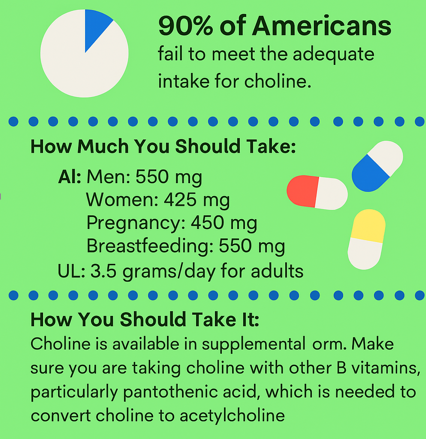
How Much Choline Do You Need? (U.S. guidelines)
There isn’t an RDA, but the U.S. Food and Nutrition Board set Adequate Intakes (AI) to prevent deficiency: generally ~425 mg/day for women and ~550 mg/day for men (higher in pregnancy/lactation). Most Americans fall short of these intakes from food alone, so building a choline-smart grocery list helps. Office of Dietary Supplements
The 7 Best Choline-Rich Foods
All nutrition figures below reflect typical U.S. servings from NIH/USDA tables; variability occurs by brand and preparation. Use these as practical estimates.
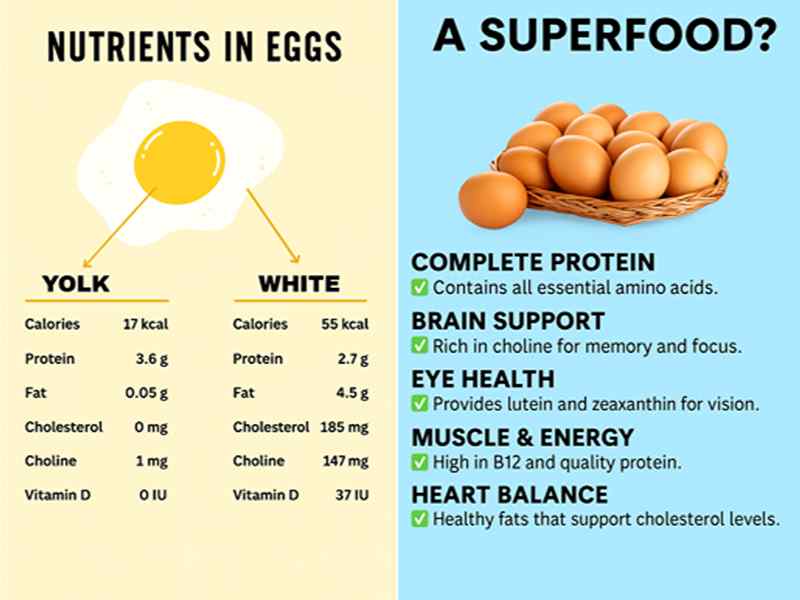
1) Eggs
- Why they help: One large whole egg delivers about 147 mg of choline, mainly in the yolk—a fast track toward your daily goal. Office of Dietary Supplements
- Easy U.S. swaps: Breakfast scramble with spinach; hard-boiled eggs for lunch boxes; a veggie-loaded frittata for Sunday meal prep.
- Smart tip: If you’re watching heart health, pairing eggs with vegetables (instead of processed meats) fits modern guidance and preserves nutrients like choline and B12. Verywell Health
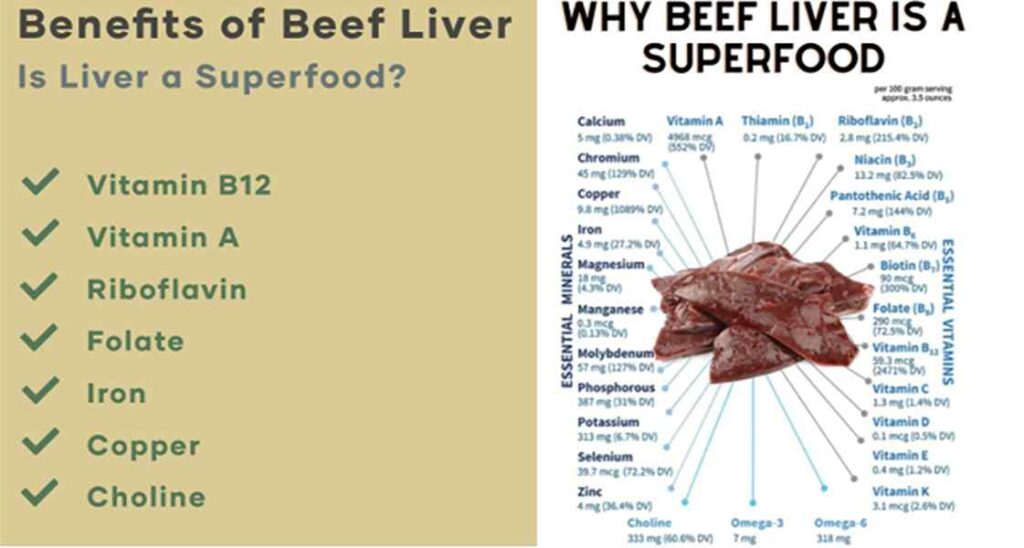
2) Beef Liver
- Why it helps: Top of the charts—~356 mg choline per 3 oz cooked. Even occasional servings move the needle. (It’s also packed with B-vitamins and iron.) Office of Dietary Supplements
- U.S. prep ideas: Sauté with onions; blend a small amount into chili or meatloaf for a nutrient boost.
- Note: Liver is nutrient-dense (notably vitamin A). Rotate with other proteins if you’re not used to it.
3) Salmon & White Fish
- Why they help: Salmon, cod, and other fish contribute meaningful choline while delivering omega-3s (salmon) for overall brain support. Example: cod ~71 mg/3 oz. Office of Dietary Supplements
- U.S. prep ideas: Sheet-pan salmon with broccoli; fish tacos with cabbage slaw; tuna-and-bean salad for a budget-friendly lunch.
- Bonus: Canned salmon is pantry-ready and affordable.

4) Chicken Breast
- Why it helps: Lean, versatile, and accessible—~72 mg choline per 3 oz roasted. Great for high-protein meal prep. Office of Dietary Supplements
- U.S. prep ideas: Grilled chicken bowls with brown rice and Brussels sprouts; rotisserie-style chicken wraps with veggies.

5) Shrimp
- Why it helps: Cooked shrimp can contribute roughly ~115 mg per 3 oz—a handy, low-calorie way to bump up choline. My Food Data
- U.S. prep ideas: Shrimp stir-fry with edamame; shrimp Caesar (use a lighter dressing); shrimp and veggie skewers.

6) Soybeans & Edamame
- Why they help: Plant-forward and budget-friendly. Roasted soybeans ~107 mg per ½ cup; edamame adds a steady contribution in a cup of pods. Office of Dietary Supplements+1
- U.S. prep ideas: Frozen edamame tossed with sea salt; soybean/edamame added to grain bowls or noodle salads.

7) Cruciferous Veggies
- Why they help: Broccoli (~31–62 mg per ½–1 cup cooked) and Brussels sprouts (~32–63 mg per ½–1 cup) offer plant-based choline plus fiber and phytonutrients—ideal as the “green half” of your plate. Office of Dietary Supplements+1
- U.S. prep ideas: Roast broccoli with garlic; shred Brussels sprouts into a lemon-Parmesan salad; add cauliflower rice to burrito bowls.

A Real-World Celebrity Snapshot
Joe Rogan (comedian, UFC commentator, and YouTuber/podcaster) has publicly shared “elk and eggs for breakfast,” highlighting a practical, protein-forward plate many Americans already enjoy. While he didn’t cite choline specifically, eggs (a staple in that meal) are a leading choline source—demonstrating how public figures often lean on simple, whole-food breakfasts that also happen to support brain nutrition. facebook.com

Simple U.S. Meal Ideas (No Supplements Needed)
- 5-Minute Breakfast: 2 eggs scrambled with leftover broccoli + whole-grain toast (≈300 mg+ choline from eggs alone). Office of Dietary Supplements
- Workday Lunch: Salmon pouch + quinoa + edamame + lemon-olive oil vinaigrette. Office of Dietary Supplements+1
- Budget Dinner: Chicken breast tacos with cabbage slaw; side of roasted Brussels sprouts. Office of Dietary Supplements
- Snack: Hard-boiled egg or a handful of roasted soybeans. Office of Dietary Supplements
10+ Quick Q&A
1) What does choline actually do for the brain?
It helps make acetylcholine, the neurotransmitter tied to memory and focus, and supports cell membranes in brain tissue. Office of Dietary Supplements
2) How much choline do U.S. adults need daily?
General AI: ~425 mg/day for women and ~550 mg/day for men (higher in pregnancy/lactation). Office of Dietary Supplements
3) What’s the easiest way to meet choline needs without supplements?
Start with eggs (≈147 mg each). Add fish, chicken, shrimp, soy/edamame, and cruciferous veggies during the week. Office of Dietary Supplements+2My Food Data+2
4) Are egg yolks necessary?
Yes—most of an egg’s choline is in the yolk. Consider pairing eggs with vegetables to keep the meal heart-smart. Office of Dietary Supplements+1
5) Is beef liver “too much” for everyday?
It’s extremely nutrient-dense (~356 mg choline/3 oz). Many people enjoy it occasionally and rotate other proteins. Consult your clinician if you have vitamin A or iron concerns. Office of Dietary Supplements
6) What if I’m pescatarian or vegetarian?
Fish (like cod or salmon) and soy foods/edamame are strong options; broccoli/Brussels sprouts help too. Office of Dietary Supplements+1
7) Do most Americans get enough choline?
No. Analyses show many U.S. adults fall short of the AI from food alone. Building menus with the foods above helps. Office of Dietary Supplements
8) Can I rely on “superfoods” alone?
No single food covers everything. A balanced pattern—lean proteins, fish, eggs, legumes/soy, whole grains, vegetables—works best. Office of Dietary Supplements
9) Are there official U.S. nutrient tables I can check?
Yes: USDA FoodData Central (search specific foods) and NIH’s Table 2 for quick choline estimates. FoodData Central+1
10) Any research linking choline intake and cognition in older adults?
Emerging studies explore associations between dietary choline and cognitive measures in older adults; evidence is still developing and should be interpreted with care. PMC
11) Are plant sources meaningful?
Yes. Soybeans/edamame and cruciferous veg contribute choline—and bring fiber and phytonutrients along for the ride. Office of Dietary Supplements+1
12) What about cholesterol and eggs?
Recent guidance allows moderate egg intake within heart-healthy patterns; pair them with vegetables instead of processed meats. Talk to your clinician for personal advice. Verywell Health
Sources & Further Reading
- NIH Office of Dietary Supplements—Choline (Health Pros Fact Sheet) — science background, AIs, and Table 2 of foods.
ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Choline-HealthProfessional Office of Dietary Supplements - USDA FoodData Central — search any grocery item for its nutrient profile.
fdc.nal.usda.gov FoodData Central - USDA/ARS Choline Database (PDF) — granular choline values across foods (incl. egg ≈147 mg/large).
nal.usda.gov/sites/default/files/page-files/choline.pdf National Agricultural Library - Oregon State—Linus Pauling Institute: Choline — additional food-source table (broccoli/Brussels sprouts).
lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/other-nutrients/choline Linus Pauling Institute - Cleveland Clinic: Choline-Rich Foods — practical overview of real-food sources.
health.clevelandclinic.org/choline-foods Cleveland Clinic - MyFoodData: High-Choline Foods — searchable, transparent data summaries (shrimp ≈115 mg/3 oz).
myfooddata.com/articles/high-choline-foods.php My Food Data - Peer-reviewed (open-access): Associations between dietary choline and cognitive measures in older adults.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC12482226 PMC - Context on eggs & heart health (consumer health explainer) — moderate intake in heart-healthy patterns.
verywellhealth.com/what-to-know-eggs-cholesterol-heart-health-7965807 Verywell Health - Celebrity snapshot (original post): Joe Rogan’s “elk and eggs” breakfast photo.
facebook.com/JOEROGAN/photos/…/10155030889009902/









Wow! Thank you! I continually needed to write on my blog something like that. Can I take a fragment of your post to my website?